What is LAMP ?
LAMP is a combination of operating system and open-source software stack.
The acronym LAMP is derived from first letters of Linux,
1- Apache 'HTTP' Server
2- MySQL database,
3- PHP/Perl/Python.
4- phpadmin
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LAMP_(software_bundle)
Server Details-
OS- Centos 6.4
Hostname- server.ashu.com
IP Add- 192.168.1.10/24
Step- 1 Change Hostname and IP Address..
1- First Check and change Hostname..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/networkHOSTNAME=server.ashu.com
2- Set Ip Address..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
---------------------------------------------------------------
DEVICE="eth0"IPADDR=192.168.1.10
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
HWADDR="00:16:D4:39:5B:6F"
NM_CONTROLLED="yes"
ONBOOT="yes"
----------------------------------------------------------------
3- Restart Network Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service network restart
[root@server ashutosh]# ifconfig
[root@server ashutosh]# hostname
Step-2 Install Apache Package and Configure...
Apache is an open-source multi-platform web server. It provides a full range
of web server features including CGI, SSL and virtual domains.
1- Install apache 'httpd' package..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install httpd -y
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
[root@server ashutosh]# chkconfig httpd on
2- Now allow apache server default port 80 through your firewall/router if you want to connect
other system..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Note- Add the following line.
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEP
3- Restart IPTables Service
[root@server ashutosh]# service iptables restart
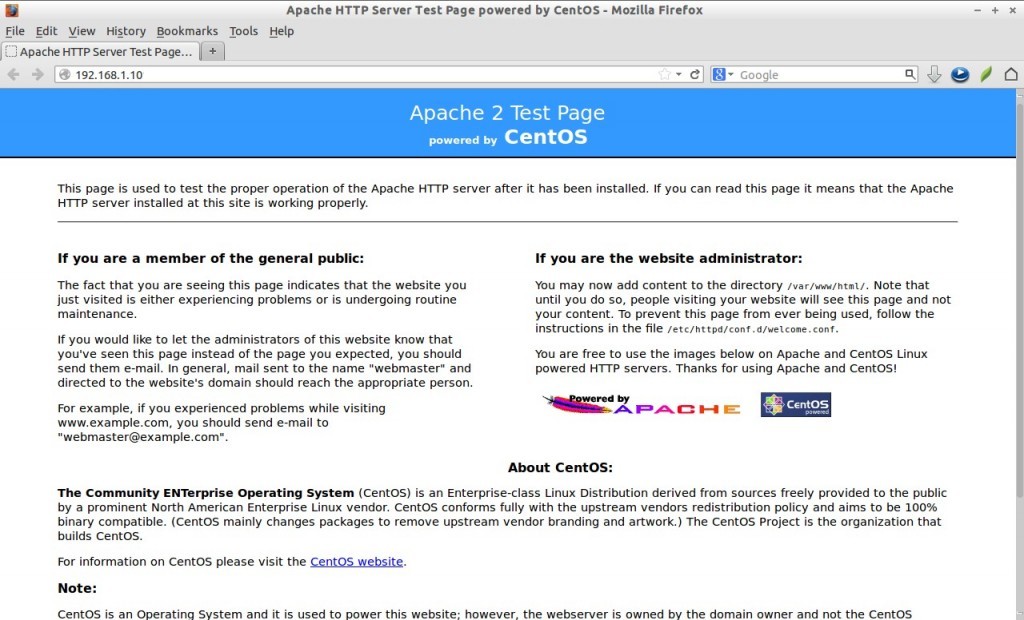
4- Test the apache server..
Open Web Browser and type..
http://server.ashu.com
orhttp://192.168.1.10
Now Sucessfully open Apache test page..
Step-3 Install and configure MySQL
MySQL is an enterprise class, open source, world’s second most used database.
MySQL is a popular choice of database for use in web applications, and is a central
component of the widely used LAMP open source web application software stack.
1- Install Mysql Package and restart service..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install mysql mysql-server -y
[root@server ashutosh]# service mysqld start
[root@server ashutosh]# chkconfig mysqld on
2- Setup MySQL root password
Note- By default, mysql root user doesn’t has password. To secure mysql,
we have to setup mysql root user password.
[root@server ashutosh]# mysql_secure_installation
-----------------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MySQL
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MySQL to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MySQL, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): --> Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MySQL
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
New password: --> Enter new password
Re-enter new password: --> Re-enter new password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MySQL
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MySQL!
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Step- 4 Install and xonfigure PHP
PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely used open-source
general purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and
can be embedded into HTML.
1- Install PHP Package..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install php -y
2- Now test php..
Create a sample “testphp.php” file in Apache document root folder and append
the lines as shown below:
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /var/www/html/testphp.php
-----------------------------------
phpinfo();
?>
-----------------------------------
3- Restart httpd Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
4- open web browser and type..
http://102.168.1.10/testphp.php
Now It will display all the details about php such as version,
build date and commands etc.
Note-
If you wanna to get MySQL support in your PHP, you should install “php-mysql” package.
If you want to install all php modules just you use the command “yum install php*”
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install php-mysql -y
Now open the phptest.php file in your browser using..
http://192.168.1.10/testphp.php
Step- 5 Install and configure phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a free open source web interface tool, used to manage
your MySQL databases. By default phpMyAdmin is not found in CentOS official
repositories. So let us install it using EPEL repository.
1- How To Install EPEL Repository-
(EPEL stands for Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux.)
[root@server yum.repos.d]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@server yum.repos.d]# wget http://epel.mirror.net.in/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@server yum.repos.d]# rpm -Uvh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@server yum.repos.d]# cd -[root@server ashutosh]#
Now list out the installed repositories using command:
[root@server ashutosh]# yum repolist
2- Now install phpMyAdmin
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install phpmyadmin -y
3- Configure phpMyAdmin...
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
Note- Find and comment the whole / section as shown below:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
....
.......
Alias /phpMyAdmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
#
#
# # Apache 2.4
# Require local
#
#
# # Apache 2.2
# Order Deny,Allow
# Deny from All
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
#
#
....
.......
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
4- Open “config.inc.php” file and change from “cookie” to “http” to change
the authentication in phpMyAdmin:
[root@server ashutosh]# cp /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.sample.inc.php /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
[root@server ashutosh] # vim /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
----------------------------------------------------------------
[...]
/* Authentication type */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'http';
[...]
----------------------------------------------------------------
5- Now Restart Apache Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
6- Now access the phpmyadmin console
http://192.168.1.10/phpmyadmin/
Image-1
Enter your MySQL username and password which you have given in previous steps.
In my case its “root” and “centos”.
Image-2
Now you will be redirected to the phpmyadmin dashboard.page as shown below.
Now you will able to manage your MariaDB databases from phpMyAdmin web interface.
LAMP Server Is Up And easy To Use..
More info-
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/LAMP
I Hope You Like It,
So Enjoy..
______________________________________________________________________________________
LAMP is a combination of operating system and open-source software stack.
The acronym LAMP is derived from first letters of Linux,
1- Apache 'HTTP' Server
2- MySQL database,
3- PHP/Perl/Python.
4- phpadmin
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LAMP_(software_bundle)
Server Details-
OS- Centos 6.4
Hostname- server.ashu.com
IP Add- 192.168.1.10/24
Step- 1 Change Hostname and IP Address..
1- First Check and change Hostname..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/networkHOSTNAME=server.ashu.com
2- Set Ip Address..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
---------------------------------------------------------------
DEVICE="eth0"IPADDR=192.168.1.10
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
HWADDR="00:16:D4:39:5B:6F"
NM_CONTROLLED="yes"
ONBOOT="yes"
----------------------------------------------------------------
3- Restart Network Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service network restart
[root@server ashutosh]# ifconfig
[root@server ashutosh]# hostname
Step-2 Install Apache Package and Configure...
Apache is an open-source multi-platform web server. It provides a full range
of web server features including CGI, SSL and virtual domains.
1- Install apache 'httpd' package..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install httpd -y
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
[root@server ashutosh]# chkconfig httpd on
2- Now allow apache server default port 80 through your firewall/router if you want to connect
other system..
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Note- Add the following line.
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEP
3- Restart IPTables Service
[root@server ashutosh]# service iptables restart
4- Test the apache server..
Open Web Browser and type..
http://server.ashu.com
orhttp://192.168.1.10
Now Sucessfully open Apache test page..
Step-3 Install and configure MySQL
MySQL is an enterprise class, open source, world’s second most used database.
MySQL is a popular choice of database for use in web applications, and is a central
component of the widely used LAMP open source web application software stack.
1- Install Mysql Package and restart service..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install mysql mysql-server -y
[root@server ashutosh]# service mysqld start
[root@server ashutosh]# chkconfig mysqld on
2- Setup MySQL root password
Note- By default, mysql root user doesn’t has password. To secure mysql,
we have to setup mysql root user password.
[root@server ashutosh]# mysql_secure_installation
-----------------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MySQL
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MySQL to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MySQL, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): --> Press Enter
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MySQL
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
New password: --> Enter new password
Re-enter new password: --> Re-enter new password
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] --> Press Enter
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MySQL
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MySQL!
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Step- 4 Install and xonfigure PHP
PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely used open-source
general purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and
can be embedded into HTML.
1- Install PHP Package..
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install php -y
2- Now test php..
Create a sample “testphp.php” file in Apache document root folder and append
the lines as shown below:
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /var/www/html/testphp.php
-----------------------------------
phpinfo();
?>
-----------------------------------
3- Restart httpd Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
4- open web browser and type..
http://102.168.1.10/testphp.php
Now It will display all the details about php such as version,
build date and commands etc.
Note-
If you wanna to get MySQL support in your PHP, you should install “php-mysql” package.
If you want to install all php modules just you use the command “yum install php*”
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install php-mysql -y
Now open the phptest.php file in your browser using..
http://192.168.1.10/testphp.php
Step- 5 Install and configure phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a free open source web interface tool, used to manage
your MySQL databases. By default phpMyAdmin is not found in CentOS official
repositories. So let us install it using EPEL repository.
1- How To Install EPEL Repository-
(EPEL stands for Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux.)
[root@server yum.repos.d]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@server yum.repos.d]# wget http://epel.mirror.net.in/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@server yum.repos.d]# rpm -Uvh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@server yum.repos.d]# cd -[root@server ashutosh]#
Now list out the installed repositories using command:
[root@server ashutosh]# yum repolist
2- Now install phpMyAdmin
[root@server ashutosh]# yum install phpmyadmin -y
3- Configure phpMyAdmin...
[root@server ashutosh]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
Note- Find and comment the whole / section as shown below:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
....
.......
Alias /phpMyAdmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
#
#
# # Apache 2.4
# Require local
#
#
# # Apache 2.2
# Order Deny,Allow
# Deny from All
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
#
#
....
.......
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
4- Open “config.inc.php” file and change from “cookie” to “http” to change
the authentication in phpMyAdmin:
[root@server ashutosh]# cp /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.sample.inc.php /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
[root@server ashutosh] # vim /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
----------------------------------------------------------------
[...]
/* Authentication type */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'http';
[...]
----------------------------------------------------------------
5- Now Restart Apache Service..
[root@server ashutosh]# service httpd restart
6- Now access the phpmyadmin console
http://192.168.1.10/phpmyadmin/
Image-1
Enter your MySQL username and password which you have given in previous steps.
In my case its “root” and “centos”.
Image-2
Now you will be redirected to the phpmyadmin dashboard.page as shown below.
Now you will able to manage your MariaDB databases from phpMyAdmin web interface.
LAMP Server Is Up And easy To Use..
More info-
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/LAMP
I Hope You Like It,
So Enjoy..
______________________________________________________________________________________